© 2025 Condenser Coil All rights reserved.
This article dives deep into the world of condenser coils, a crucial component of any HVAC system, exploring their function, design, and key features. It also contrasts them with evaporator coils to highlight their unique roles in the refrigeration cycle. Understanding how these super radiator coils work is essential for anyone who wants to maximize their air conditioning system’s efficiency and longevity. This article is worth reading because it provides an in-depth look at a component that is often overlooked but is critical to your comfort. It will help you make informed decisions on maintenance and repair, as well as prepare you for frequently asked questions about AC units.
The condenser is a vital component of any refrigeration system, including your home air conditioner. It’s part of the outdoor unit and is responsible for releasing the heat absorbed by the refrigerant from your indoor space to the outdoor air. Think of it as the “heat dumping” station of your ac unit. The function of the condenser is to release heat.
The condenser works in conjunction with the compressor, the evaporator coil, and an expansion device, which are the other major components of a typical air conditioning system. The refrigeration system is what keeps your house cool. The condenser plays a vital role in the cycle. Its primary function is to convert the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant vapor that leaves the compressor back into a liquid state. This process, known as condensation, releases the heat that was absorbed from the indoor air. The condenser is essential to keeping your house cool.
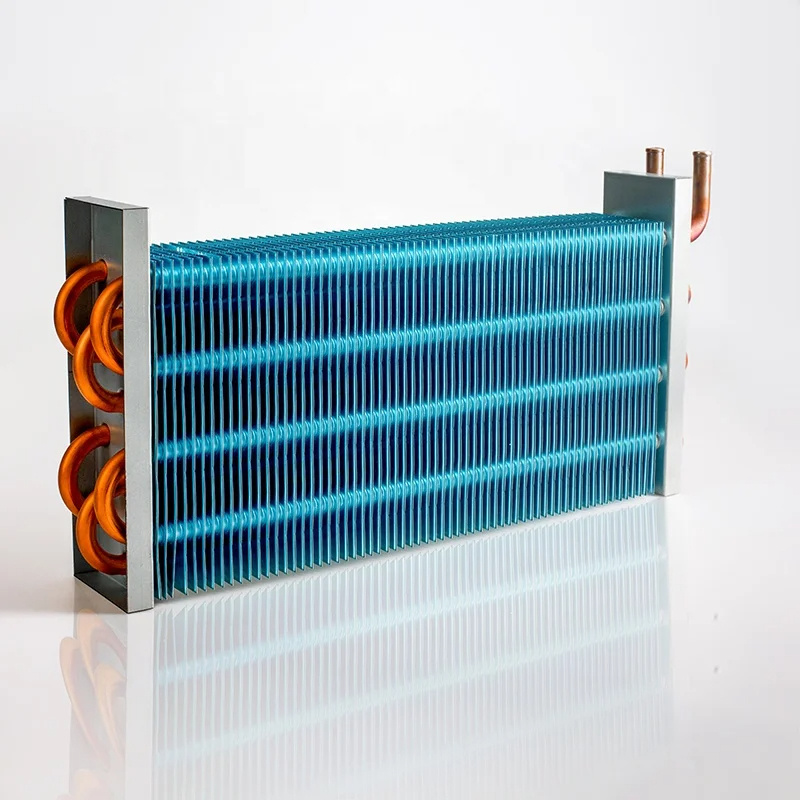
The condenser coil is the heart of the condenser unit. The condenser coil is where the heat rejection process occurs. Its coil function can be summarized as follows:
The condenser coil is engineered to maximize heat transfer efficiency. The coil’s design, including the diameter of the copper tubes, the spacing and design of the fins, and the overall airflow pattern, all play a crucial role in its performance. Condenser coils are used in many different applications. The refrigerant velocity also affects how the coil works.
The design of a condenser coil is a critical factor in the overall performance and efficiency of an air conditioning system. Engineers carefully consider various factors when designing these coils to optimize their heat transfer capabilities and ensure durability. Here are some key coil design considerations:
The evaporator coil is the counterpart to the condenser coil in your air conditioning system. While the condenser coil releases heat to the outside, the evaporator coil‘s primary function is to absorb heat from the indoor air, thus cooling your home. It is one of the two heat exchangers in the system.
Here’s how the evaporator coil works:
The evaporator coil is typically made of copper tubes with aluminum fins to enhance heat transfer. The coil’s design and the refrigerant’s properties are carefully engineered to maximize the amount of heat absorbed from the indoor air. The evaporator is one of the most important parts of the cooling system.
While both the condenser coil and the evaporator coil are essential components of your air conditioning system and work together to cool your home, they have distinct functions and characteristics. Here’s a table summarizing their key differences:
| Feature | Condenser Coil | Evaporator Coil |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Outdoor unit | Indoor unit (air handler or furnace) |
| Primary Function | Releases heat to the outdoor air | Absorbs heat from the indoor air |
| Refrigerant State | High-pressure gas to high-pressure liquid | Low-pressure liquid to low-pressure gas |
| Temperature | Hot | Cold |
| Airflow | Outdoor air is blown across the coil by a fan | Indoor air is blown across the coil by the air handler’s blower |
| Common Issues | Dirt and debris buildup, fin damage, corrosion, refrigerant leaks | Dirt and debris buildup, refrigerant leaks, ice formation, airflow restrictions |
| Materials | Typically made of copper tubes with aluminum fins; spine fin coils (aluminum fins wound around copper tubes) also used | Typically made of copper or aluminum tubes with aluminum fins |
| Design | Designed to maximize heat rejection to the outdoor air; various designs including tube-and-fin, spine fin, and microchannel coils | Designed to maximize heat absorption from the indoor air; common designs include A-coils, N-coils, and slab coils |
Understanding these differences can help you appreciate the unique roles that each coil plays in the refrigeration system. The condenser coil must be kept clean, and free of debris.
The condenser and evaporator coils work in a continuous, closed-loop cycle known as the compression-expansion refrigeration cycle. They are the two essential heat exchangers in this process, working in tandem to transfer heat from the inside of your home to the outside. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how they work together:
This continuous cycle of evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion allows your air conditioning system to effectively remove heat from your home and keep your space being conditioned cool and comfortable.
While the fundamental function of evaporator and condenser coils remains the same, there are variations in their design and construction. Here are some common types of coils found in AC systems:
The specific type of coil used in your air conditioner depends on factors such as the manufacturer, the model, the system’s capacity, and its intended application. Different types of coils work best for different applications.
Proper maintenance of your condenser and evaporator coils is crucial for ensuring the efficiency, longevity, and reliable performance of your air conditioning system. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
Condenser Coil Cleaning:
Evaporator Coil Cleaning:
Air Filter Replacement: Regularly replacing your air conditioner’s air filter is crucial for preventing dirt and debris from reaching the evaporator coil. A clogged filter restricts airflow, making your system work harder and potentially leading to coil issues.
While regular cleaning and basic maintenance can be performed by homeowners, certain situations require the expertise of a qualified HVAC professional. It is important to schedule an appointment with a professional if you experience issues. Contact a professional if you notice any of the following:
Attempting to repair complex AC issues yourself can be dangerous and may void your system’s warranty. When in doubt, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and consult with a qualified HVAC professional.
Here are some answers to frequently asked questions about AC coils:
Q: How long do evaporator and condenser coils last?
A: With proper maintenance, evaporator and condenser coils can last 10-15 years or even longer. However, their lifespan can be shortened by factors such as corrosion, physical damage, and lack of regular cleaning.
Q: Can I replace just one coil, or do I need to replace both?
A: In most cases, it’s possible to replace just the faulty coil, whether it’s the evaporator or the condenser. However, if your AC system is older or if both coils are showing signs of wear, your HVAC technician may recommend replacing both for optimal performance and efficiency.
Q: How much does it cost to replace AC coils?
A: The cost to replace AC coils varies depending on factors like the type of coil, the brand of your AC system, and labor rates in your area. Evaporator coil replacement typically costs between $600 and $2,000, while condenser coil replacement can range from $700 to $2,500 or more.
Q: Can I use a pressure washer to clean my condenser coil?
A: It’s generally not recommended to use a pressure washer on your condenser coil, as the high-pressure water can easily damage the delicate fins. A garden hose with a gentle spray nozzle is a safer and more effective option.
Q: What type of coil cleaner should I use?
A: It’s best to use a commercial coil cleaner specifically designed for air conditioning coils. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Avoid using harsh chemicals or bleach, as they can damage the coils. If you need help, you can contact us for more information.
Q: How often should I have my AC coils inspected by a professional?
A: It’s recommended to have your entire AC system, including the coils, inspected and serviced by a qualified HVAC technician at least once a year, preferably in the spring before the cooling season begins.
| Feature | Evaporator Coil | Condenser Coil |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Inside the home, typically within the air handler or furnace | Outside the home, within the outdoor condenser unit |
| Primary Function | Absorbs heat from indoor air | Releases heat to the outdoor air |
| Refrigerant State | Low-pressure liquid to low-pressure gas (evaporation) | High-pressure gas to high-pressure liquid (condensation) |
| Temperature | Cold | Hot |
| Airflow | Indoor air is blown across the coil by the air handler’s blower | Outdoor air is blown across the coil by the condenser fan |
| Common Issues | Dirt and debris buildup, refrigerant leaks, ice formation, airflow restrictions | Dirt and debris buildup, fin damage, corrosion, refrigerant leaks |
| Materials | Typically made of copper or aluminum tubes with aluminum fins | Typically made of copper tubes with aluminum fins; spine fin coils (aluminum fins wound around copper tubes) also used |
| Design | Designed to maximize heat absorption from the indoor air; common designs include A-coils, N-coils, and slab coils | Designed to maximize heat rejection to the outdoor air; various designs including tube-and-fin, spine fin, and microchannel coils |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning, air filter replacement, professional inspection | Regular cleaning, clearing surrounding area, professional inspection |
| Function | Absorbs heat from the air in your house, cooling the air that is then circulated throughout your home. | Releases the absorbed heat from the refrigerant to the outdoor air, turning the refrigerant back into a liquid for the next cycle. |
| Refrigerant enters the evaporator as a low-pressure liquid. | The hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas then enters the condenser coil in the outdoor unit. | |
| The function of the evaporator coil is to absorb heat. | The function of the condenser coil is to release heat. | |
| The evaporator coil is located inside, near the air handler. | The condenser coil is typically located outside, near the evaporator. | |
| The evaporator coil is essential for removing heat. | The air conditioner’s condenser is essential for releasing heat. | |
| The evaporator coil is cold to the touch. | The condenser coil is hot to the touch. | |
| Evaporator coils are made of materials designed for efficient heat exchange. | Condenser coils are made of copper or aluminum, often with aluminum fins to increase surface area. | |
| Evaporator coil issues can include reduced cooling capacity and unusual noises. | Condenser coil issues include corrosion and leaks. | |
| Evaporator coil maintenance includes cleaning. | Condenser coil maintenance includes cleaning. | |
| A well-maintained evaporator coil improves cooling efficiency. | A well-maintained condenser coil improves cooling efficiency. | |
| The evaporator coil absorbs heat. | The condenser coil releases heat. |
By familiarizing yourself with the intricacies of your air conditioner’s condenser and evaporator coils, you’re taking a significant step towards becoming a more informed and proactive homeowner. Remember, a well-maintained HVAC system not only ensures your comfort but also contributes to lower energy bills and a reduced environmental impact. You should never be left out in the cold because your AC is not working.

This article delves into the common problem of refrigerant leaks in LG split AC units, specifically focusing on the debate between aluminum and copper condenser coils.

Your air conditioning unit is a complex system with many parts working together to keep your home cool and comfortable.

This numerical investigation delves into the influence of geometric parameters of immersed helical condenser coils.

This article explains how water chillers work, focusing on the role of water in the cooling process.

Air-cooled condenser coils are integral constituents of air conditioning and refrigeration apparatuses.

This article explores the crucial relationship between evaporator and condenser coils in your AC system, focusing on the importance of their size ratio for optimal performance in residential air conditioning.

This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to effectively clean your refrigerator’s condenser coils.

Your air conditioner is a lifesaver during hot summer months, providing welcome relief from the heat.

This article provides a comprehensive overview of AC evaporator coil replacement cost, as well as condenser coil replacement cost, helping homeowners understand what to expect when facing this type of repair.

The escalating global energy demand, coupled with a growing awareness of environmental sustainability.

Your air conditioner is a crucial part of your home comfort, especially during hot weather.

This document elucidates the principal factors influencing thermal exchange between the refrigerant and the airstream within a plate finned-tube heat exchanger

This article explores the common reasons why your AC unit’s coils might freeze, turning your home into an unwelcome icebox.
© 2025 Condenser Coil All rights reserved.
Fill out the form below, our team can reply in 20 minutes.